Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1362-1367.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.09.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Postoperative coronal plane imbalance and model construction for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Li Shi-hao, Deng Qiang, Xun Chuan-hui, Sheng Wei-bin
- Department of Spinal Surgery (Department of Orthopedics), First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2014-02-26Published:2014-02-26 -
Contact:Sheng Wei-bin, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Spinal Surgery (Department of Orthopedics), First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Shi-hao, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Spinal Surgery (Department of Orthopedics), First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shi-hao, Deng Qiang, Xun Chuan-hui, Sheng Wei-bin . Postoperative coronal plane imbalance and model construction for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(9): 1362-1367.
share this article
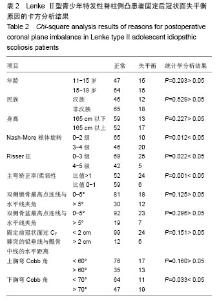
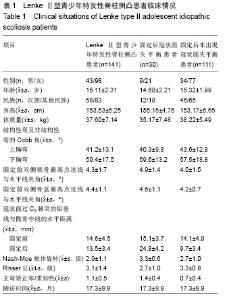
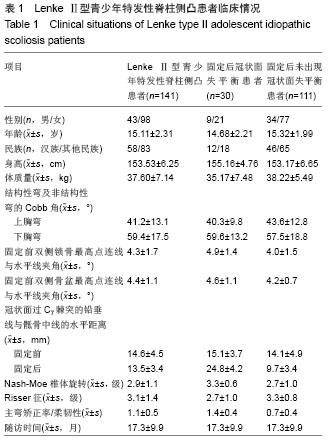
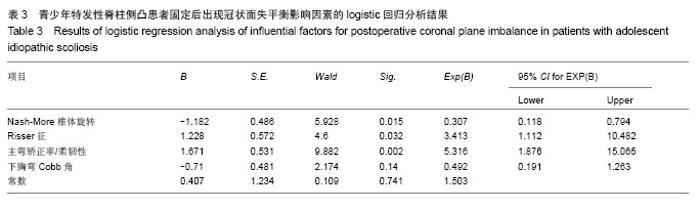
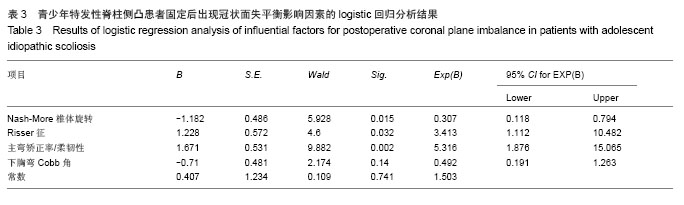
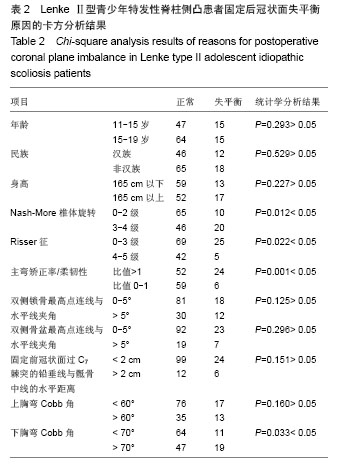
分别以年龄、性别、民族、身高、椎体旋转、Risser征、上胸弯Cobb角、下胸弯Cobb角、主弯矫正率/柔韧性、固定前双侧锁骨最高点连线与水平线夹角、固定前双侧骨盆最高点连线与水平线夹角、固定前固定前及固定后冠状面过C7棘突的铅垂线与骶骨中线的水平距离、上下胸弯Cobb角等行卡方检验比较各组间各数据差异,结果发现患者年龄、民族、身高、双侧锁骨最高点连线与水平线夹角、双侧骨盆最高点连线与水平线夹角、固定前冠状面过C7棘突的铅垂线与骶骨中线的水平距离、上胸弯Cobb角对固定后是否会出现冠状面失平衡没有影响,而冠状面失平衡患者椎体旋转、Risser征、主弯矫正率/柔韧性、下胸弯Cobb角与其他患者的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05;表2)。"
| [1]Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(8):1169-1181.[2]乔军,朱泽章,刘臻,等.性别差异对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸SRS-22问卷评分的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(2): 157-160.[3]上海长海医院骨科.脊柱侧凸诊疗问答(十)[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(19):2011.[4]Stokes OM, Luk KD. The current status of bracing for patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B (10):1308-1316. [5]Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(8):1097-1106.[6]徐宏光,赵泉来,王弘,等.成人退变性腰椎侧凸个体化治疗方案的选择[J].解剖与临床,2012,17(3):189-193.[7]王飞,何翔,李明.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者术前柔韧性评估的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(19):1966-1969.[8]Miyanji F, Slobogean GP, Samdani AF, et al. Is larger scoliosis curve magnitude associated with increased perioperative health-care resource utilization?: a multicenter analysis of 325 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis curves. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(9):809-813. [9]Haber LL, Hughes JD, Thompson GH, et al. Long-term retrospective of the Kaneda anterior scoliosis system in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(4):362-367. [10]Li M, Shen Y, Gao ZL, et al. Surgical treatment of adult idiopathic scoliosis: long-term clinical radiographic outcomes. Orthopedics. 2011;34(3):180. [11]Bharucha NJ, Lonner BS, Auerbach JD, et al. Low-density versus high-density thoracic pedicle screw constructs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: do more screws lead to a better outcome? Spine J. 2013;13(4):375-381. [12]Tsirikos AI, Subramanian AS. Posterior spinal arthrodesis for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using pedicle screw instrumentation: does a bilateral or unilateral screw technique affect surgical outcome? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(12): 1670-1677.[13]Ughwanogho E, Patel NM, Baldwin KD, et al. Computed tomography-guided navigation of thoracic pedicle screws for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis results in more accurate placement and less screw removal. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(8):E473-478. [14]Min K, Sdzuy C, Farshad M. Posterior correction of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with pedicle screw instrumentation: results of 48 patients with minimal 10-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(2):345-354. [15]Sugarman E, Sarwahi V, Amaral T, et al. Comparative analysis of perioperative differences between hybrid versus pedicle screw instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(3):161-166. [16]Yilmaz G, Borkhuu B, Dhawale AA, et al. Comparative analysis of hook, hybrid, and pedicle screw instrumentation in the posterior treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(5):490-499. [17]Qian B, Jiang J, Zhu F, et al. How is the trachea at risk of injury from pedicle screw insertion in proximal thoracic curve of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients? Eur Spine J. 2013;22(2):338-344. [18]Liu J, Shen J, Zhang J, et al. The position of the aorta relative to the spine for pedicle screw placement in the correction of idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(4):E103-107. [19]Hwang SW, Samdani AF, Stanton P, et al. Impact of pedicle screw fixation on loss of deformity correction in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33(4): 377-382. [20]Kuraishi S, Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, et al. Pedicle morphology using computed tomography-based navigation system in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):22-28. [21]Hwang SW, Samdani AF, Marks M, et al. Five-year clinical and radiographic outcomes using pedicle screw only constructs in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6):1292-1299. [22]Hwang SW, Samdani AF, Wormser B, et al. Comparison of 5-year outcomes between pedicle screw and hybrid constructs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(3):212-219. [23]Yang C, Wei X, Zhang J, et al. All-pedicle-screw versus hybrid hook-screw instrumentation for posterior spinal correction surgery in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a curve flexibility matched-pair study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(5): 633-639. [24]Glotzbecker MP, Emans JB. Commentary: Does pedicle screw density matter in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Spine J. 2013;13(4):382-383. [25]Wang X, Aubin CE, Robitaille I, et al. Biomechanical comparison of alternative densities of pedicle screws for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21(6):1082-1090. [26]Blondel B, Lafage V, Farcy JP, et al. Influence of screw type on initial coronal and sagittal radiological correction with hybrid constructs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Correction priorities. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(8): 873-878. [27]Suk SI. Pedicle screw instrumentation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: the insertion technique, the fusion levels and direct vertebral rotation. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(2):89-100.[28]Dobbs MB, Lenke LG, Kim YJ, et al. Selective posterior thoracic fusions for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: comparison of hooks versus pedicle screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(20):2400-2404.[29]Liljenqvist U, Hackenberg L, Link T, et al. Pullout strength of pedicle screws versus pedicle and laminar hooks in the thoracic spine. Acta Orthop Belg. 2001;67(2):157-163.[30]Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, et al. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(18):2049-2057.[31]Suk SI, Lee SM, Chung ER, et al. Determination of distal fusion level with segmental pedicle screw fixation in single thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28(5):484-491.[32]Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(3):333-342.[33]Trobisch PD, Ducoffe AR, Lonner BS, et al. Choosing fusion levels in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(9):519-528. [34]Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, et al. Correlation between facial asymmetry, shoulder imbalance, and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthopedics. 2011;34(6):187. [35]Min K, Haefeli M, Mueller D, et al. Anterior short correction in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with mini-open thoracotomy approach: prospective clinical, radiological and pulmonary function results. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl 6: S765-772. [36]La Maida GA, Zottarelli L, Mineo GV, et al. Sagittal balance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: radiographic study of spino-pelvic compensation after surgery. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22 Suppl 6:S859-867.[37]Yang S, Feuchtbaum E, Werner BC, et al. Does anterior shoulder balance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis correlate with posterior shoulder balance clinically and radiographically? Eur Spine J. 2012;21(10):1978-1983. [38]Schülein S, Mendoza S, Malzkorn R, et al. Rasterstereographic evaluation of interobserver and intraobserver reliability in postsurgical adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(4): E143-149.[39]Karakaya I, Sismanlar SG, Atmaca H, et al. Outcome in early adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after deformity correction: assessed by SRS-22, psychometric and generic health measures. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2012;21(4):317-321. [40]Sathira-Angkura V, Pithankuakul K, Sakulpipatana S, et al. Validity and reliability of an adapted Thai version of Scoliosis Research Society-22 questionnaire for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(9):783-787. [41]Franic M, Kujundzic Tiljak M, Pozar M, et al. Anterior versus posterior approach in 3D correction of adolescent idiopathic thoracic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(7):795-802. [42]Lam TP, Ng BK, Cheung LW, et al. Effect of whole body vibration (WBV) therapy on bone density and bone quality in osteopenic girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(5): 1623-1636. [43]Vidal C, Ilharreborde B, Azoulay R, et al. Reliability of cervical lordosis and global sagittal spinal balance measurements in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6): 1362-1367.[44]Mangone M, Raimondi P, Paoloni M, et al. Vertebral rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis calculated by radiograph and back surface analysis-based methods: correlation between the Raimondi method and rasterstereography. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(2):367-371. [45]Ilharreborde B, Steffen JS, Nectoux E, et al. Angle measurement reproducibility using EOS three-dimensional reconstructions in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated by posterior instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(20):E1306-1313.[46]Roussouly P, Labelle H, Rouissi J, et al. Pre- and post-operative sagittal balance in idiopathic scoliosis: a comparison over the ages of two cohorts of 132 adolescents and 52 adults. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 2:S203-215. [47]Canavese F, Holveck J, De Coulon G, et al. Analysis of concave and convex rib-vertebral angle, angle difference, and angle ratio in patients with lenke type 1 main thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated by observation, bracing or posterior fusion, and instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(8):506-513. [48]Danielsson AJ, Hasserius R, Ohlin A, et al. Body appearance and quality of life in adult patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with a brace or under observation alone during adolescence. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(9): 755-762. [49]Sanchez-Raya J, Bago J, Pellise F, et al. Does the lower instrumented vertebra have an effect on lumbar mobility, subjective perception of trunk flexibility, and quality of life in patients with idiopathic scoliosis treated by spinal fusion? J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(8):437-442. [50]Kinel E, Kotwicki T, Podolska A, et al. Quality of life and stress level in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis subjected to conservative treatment. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012; 176:419-422.[51]Pellegrino LA, Avanzi O. Prospective Evaluation of Quality of Life in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis before and after Surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. in press.[52]Akazawa T, Minami S, Kotani T, et al. Health-related quality of life and low back pain of patients surgically treated for scoliosis after 21 years or more of follow-up: comparison among nonidiopathic scoliosis, idiopathic scoliosis, and healthy subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(22): 1899-1903. [53]Deceuninck J, Bernard JC. Quality of life and brace-treated idiopathic scoliosis: a cross-sectional study performed at the Centre des Massues on a population of 120 children and adolescents. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;55(2):93-102.[54]Gorzkowicz B. Quality of life in patients with idiopathic scoliosis treated operatively with the Cotrel-Dubousset method. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2011;57(2):25-31.[55]Watanabe K, Hasegawa K, Hirano T, et al. Use of the scoliosis research society outcomes instrument to evaluate patient outcome in untreated idiopathic scoliosis patients in Japan: part II: relation between spinal deformity and patient outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(10):1202-1205.[56]Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Baldus C, et al. Preventing decompensation in King type II curves treated with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. Strict guidelines for selective thoracic fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(8 Suppl):S274-281.[57]Puno RM, An KC, Puno RL, et al. Treatment recommendations for idiopathic scoliosis: an assessment of the Lenke classification. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(18): 2102-2115.[58]Suk SI, Lee SM, Chung ER, et al. Selective thoracic fusion with segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: more than 5-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(14):1602-1609.[59]Little DG, Song KM, Katz D, et al. Relationship of peak height velocity to other maturity indicators in idiopathic scoliosis in girls. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(5):685-693.[60]McCance SE, Denis F, Lonstein JE, et al. Coronal and sagittal balance in surgically treated adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with the King II curve pattern. A review of 67 consecutive cases having selective thoracic arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(19):2063-2073. |
| [1] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [3] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Zhu Zhenqi, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of sciatic scoliosis caused by lumbar disc herniation: a 2-year follow-up of coronal and sagittal balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 409-413. |
| [4] | Zhou Chen, Xing Wenhua. Application advantages of three-dimensional printing technology and finite element analysis in scoliosis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1898-1903. |
| [5] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Lin Weimin, Xu Shenggui, Huang Qilong, Guo Weizhong, Lin Chengshou. Development and biomechanical study of a new sternoclavicular hook plate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1395-1399. |
| [6] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [7] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [8] | Wu Yeke, Gao Ranran, Zuo Yuling, Yu Jianfeng, Zhao Lixing, Nie Wenhan, Zheng Tao, Ai Huangping, Yan Hang. Factors affecting the clinical success rate of miniscrew implants for orthodontic treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 538-543. |
| [9] | Zhao Dezhu, Guan Tianmin, Wu Bin, Mei Zhao. Design and implementation of an adolescent idiopathic scoliosis orthosis design expert system based on fuzzy logic [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5255-5261. |
| [10] | Li Hongke, Hao Shenshen, Wang Pengcheng, Yang Hongjie, Dong Shengli, Liu Shuai, Wang Fei, Liu Zhibin. Accuracy of 3D printing navigation template in pedicle screw placement for idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4757-4762. |
| [11] | Zhang Hui, Xu Nanwei, Nong Luming, Tang Xueming, Zhou Xindie, Jiang Wei. Factors influencing the prognosis of central cord syndrome treated with drug therapy and titanium plate fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 348-353. |
| [12] | Yang Shun, Chen Keyi, Cheng Yabo, Xiang Wang, Zhang Jing, Gu Hongji, Chi Haotian. Wrist arthroscopy-assisted titanium internal fixator for the treatment of complex distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 366-371. |
| [13] | Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [14] | Wen Wangqiang, Xu Haoxiang, Zhang Zepei, Miao Jun. Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3883-3889. |
| [15] | Zhang Han, He Bin, Wang Boyao, Qin Hu, Wang Yunhua, Fan Lei. Application of 3D printing technology in preoperative planning of scapular fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1864-1869. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||